
Whole Earth & Sea Bone Structure Multivitamin & Mineral
Bird anatomy, or the physiological structure of birds' bodies, shows many unique adaptations, mostly aiding flight.Birds have a light skeletal system and light but powerful musculature which, along with circulatory and respiratory systems capable of very high metabolic rates and oxygen supply, permit the bird to fly. The development of a beak has led to evolution of a specially adapted.

Turkey Bones Braeside
A hen or gobbler ducks its head, tucks low to the ground and darts off through the brush. Turkeys have been clocked at 10 to 12 mph. A turkey's strong, muscular legs are not only good for running, they catapult the bird into the air. Heavy-winged gobblers are strong aviators for 200 to 400 yards or so.

Bone Structure Anatomy Periosteum Spongy 3D Model
Your holiday turkey is a saurischian dinosaur, like Apatosaurus, Tyrannosaurus, and Velociraptor. The ancestors of dinosaurs had a hipbone, the pubis, which pointed forward. The pubis evolved to point backward in two groups of dinosaurs: ornithischians and birds. Even though they share the same hip shape, many other features show that birds are.
Free Bone Structure Stencil Stencil Printables Kidadl
Step 2: Examine the legs Pull one of the legs away from the body. The drumstick is the outermost part of the leg, below the knee joint. Above that is the thigh, which extends toward the back of the turkey. Step 3: Examine the wings Pull one of the wings away from the body. The drummette is the part of the wing nearest the body.

Bone Mistholme
A wild turkey can easily spot a hunter from a few hundred yards away if not properly concealed. "Turkeys have monocular periscopic vision, which means that their eyes function independently of each other to transmit information to the brain," Chamberlain said. "Because the eyes are on the sides of their heads, turkeys have an almost 360.

Turkey Neck Anatomy
The basic framework of the turkey resembles our own: backbone, long limb bones like the femur, a rib cage, etc., for the attachment and work of muscles. Yet compared to mammals like us, the bones are light and hollow, with considerable fusion — particularly in the pelvis, the back, and tail vertebrae (called the pygostyle), and at the end of.

Photo Real Turkey Skeleton Photo Isolated Stock Photo 2114369351
4. What is the bone structure of the rib cage in a turkey? The rib cage of a turkey is made up of sturdy flat bones that protect the vital organs. There are usually around 14 ribs in a turkey, joined together by cartilage. 5. Can turkey bones be used to make broth? Yes, turkey bones can be used to make flavorful and nutritious broth.

Bone Structure Anatomy Periosteum Spongy 3D Model
As with the other meats, you want to allow 6-8oz of meat per meal, and 10-12oz of meat if you want leftovers. An easy way to think about the boneless crown is that it will feed 2 people for the weight in lbs that you have bought. A 5lb boneless turkey crown will comfortably feed 10 people ( 6-8 with leftovers!).

(PDF) Bone structure Sharanya Sankar Academia.edu
The Head: The head of a turkey is a colorful cornucopia. Composed of the caruncles, wattles, snood and dewlap, all are used for different purposes. The changing of color and shape in males.
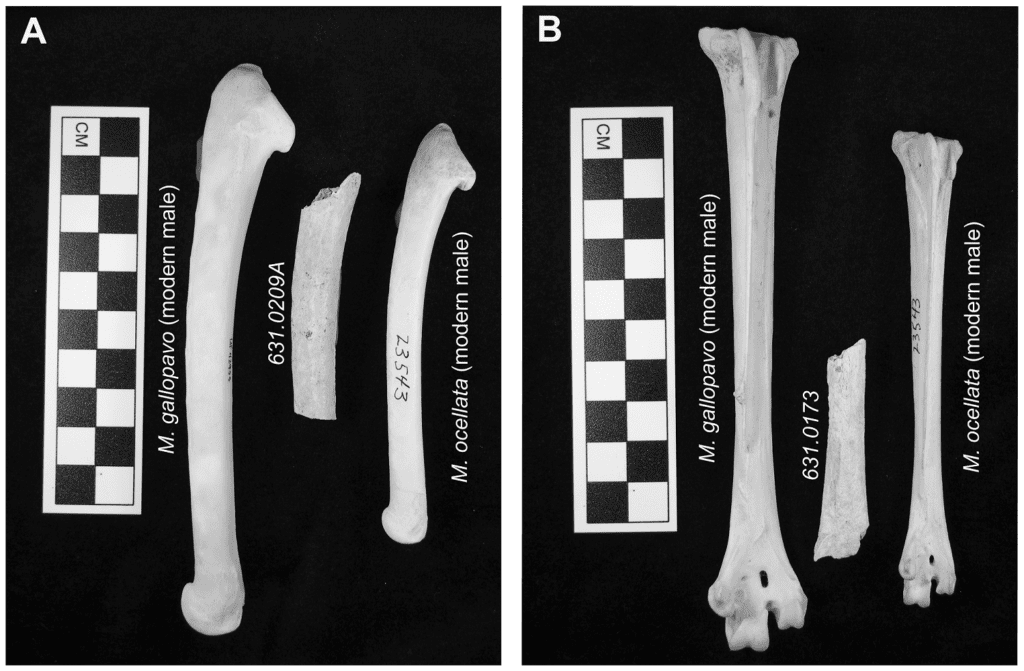
A Brief History of the Turkey Ohio History Connection
On the turkeys' landings, the muscle fibers stiffened against the impact, sending energy to the tendon, which then released it some 2.4 times more slowly back to the muscle fibers. The findings.
FileSharPei bone mouth.JPG Wikimedia Commons
The bones of birds are lighter in weight than those of mammals. Some of the bones are hollow and actually act as part of the avian respiratory system. These bones, called pneumatic bones, include the skull, humerus, clavicle, keel, pelvic girdle, and lumbar and sacral vertebrae. Other important bones in the avian skeleton are the medullary bones.

80X Magnification Human Bone Structure Model PVC Bone Marrow Structure
Additional Functions of Turkey Bones. In addition to providing structure and facilitating movement, turkey bones serve other important functions: Protection: Some bones in a turkey's body, such as the skull and ribcage, provide protection for vital organs like the brain, heart, and lungs. These bones act as a shield, safeguarding the delicate.

The Honest Kitchen Bone Broth Bites Turkey Bone Broth, Pumpkin
Turkeys have many of the same basic external parts as chickens —ears, earlobes, eyes, eye rings, beak, wings, tail, thighs, hocks, shanks, spurs, claws, and toes. However, some differences exist in the external anatomies of turkeys and chickens. For example, a turkey's head (shown in Figure 1) differs from a chicken's head in several ways.

Barbara’s Turkey Bone Broth — Barbara Barrett RD
The preservation of the domestic turkey's hind limb bone dimensions is also consistent with a plastic response. Bone remodeling has been shown to maintain similar strain levels throughout ontogeny in chickens (Biewener, Swartz, & Bertram, 1986), and turkey femur remodeling has been found to correspond with body weight (Zhong et al., 2012). If.

Bone Structure and Terminology Anatomy and Physiology YouTube
A 3-ounce serving of cooked turkey breast contains about 22 grams of protein, 3 grams of fat, and 0 grams of carbohydrates. Turkey is also a good source of niacin, vitamin B6, vitamin B12, iron, zinc, and phosphorus. Protein. Protein is an essential nutrient that is needed for the growth and repair of tissues.
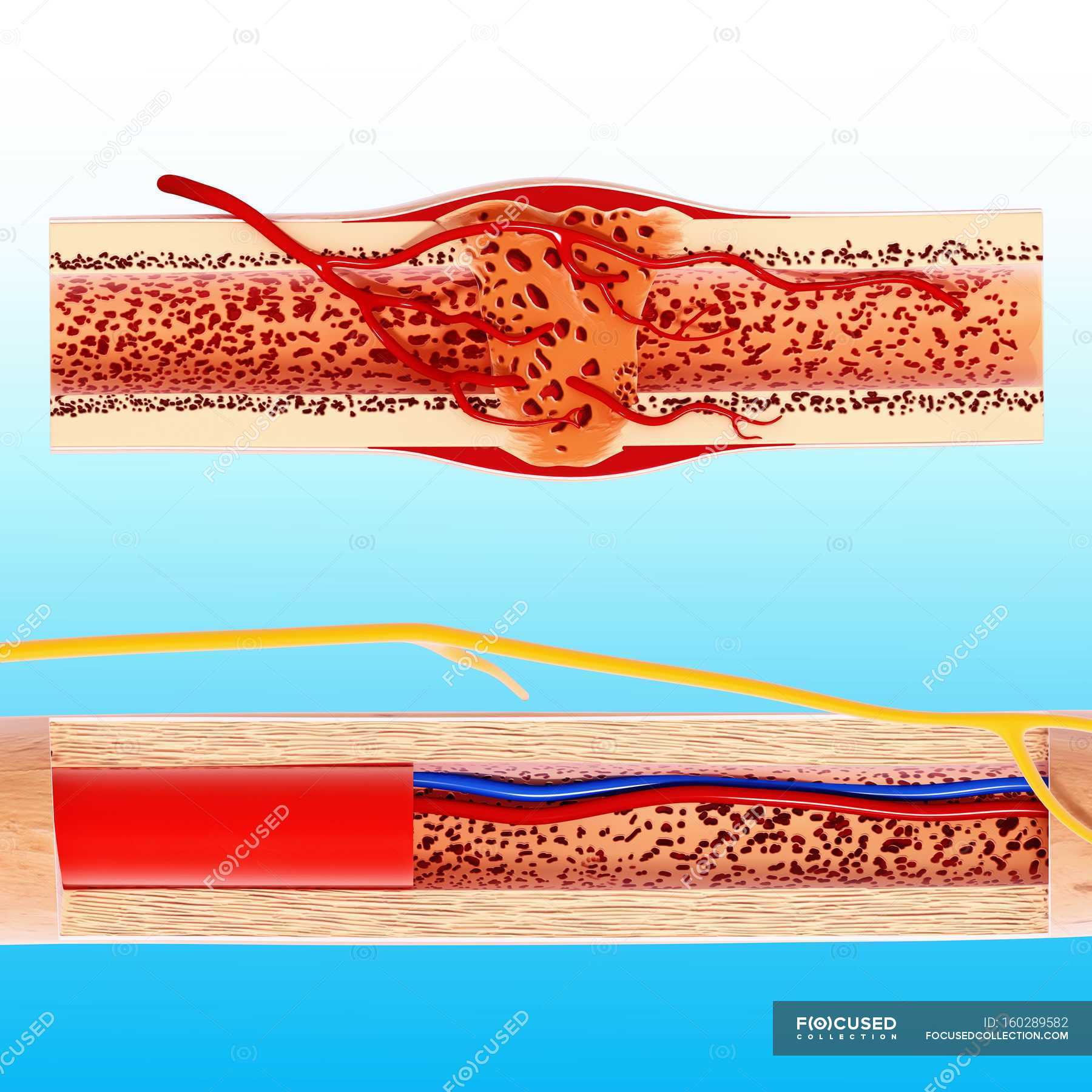
Human bone structure — anatomy, healthy Stock Photo 160289582
The Mexican turkey is the ancestor of all domestic turkeys consumed in the world today and Mesoamerica's only indigenous domesticated animal. The discovery of the bones south of the turkey's natural range shows animal exchange occurred from northern Mesoamerica to the Maya cultural region during the Late Preclassic period from 300 BC to 100 CE.