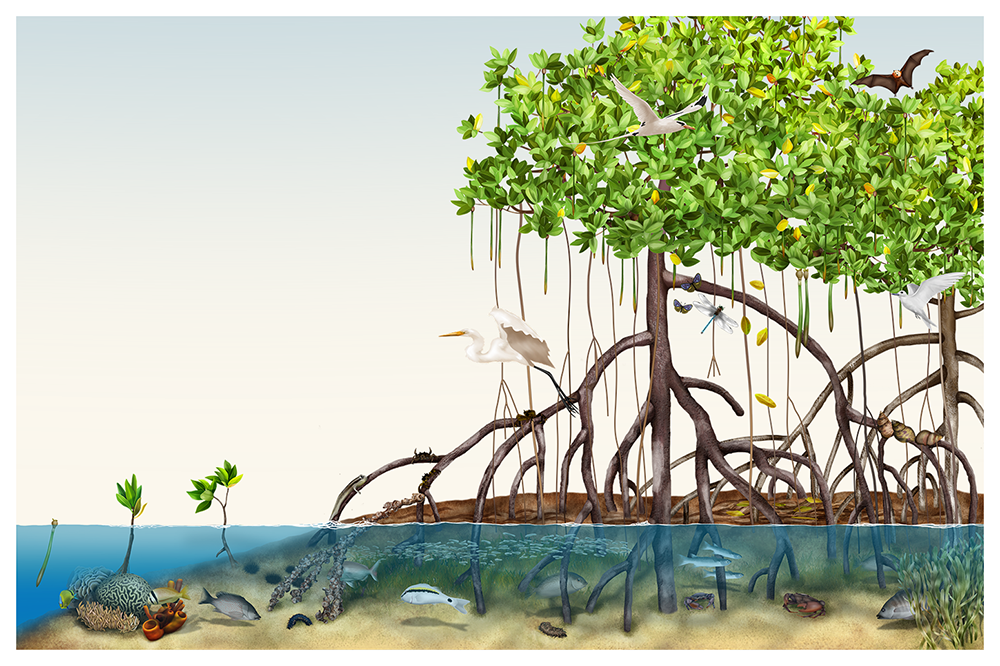

Mangrove ecosystem
The Mangrove Ecosystem. Use this infographic (provided in English, French, and Spanish) to explore mangrove ecosystem, which acts as the ocean's nursery and a barrier to coastal erosion. Grades. 5 - 12+ Subjects. Biology, Ecology, Earth Science, Oceanography.
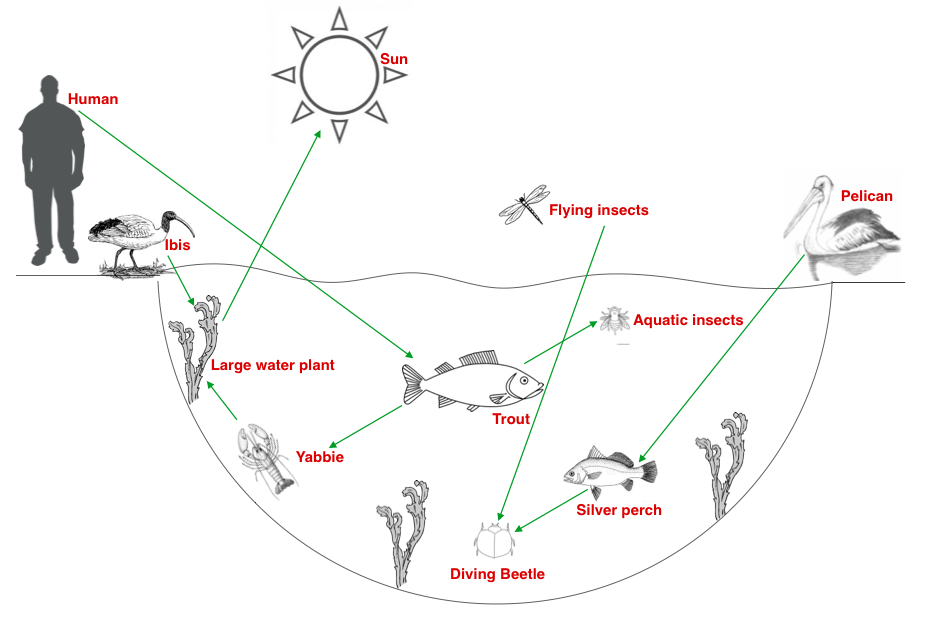
Food webs Mangroves!
This provides a food source for marine life including economically important shrimp, crabs, and fish. An estimated 75% of the game fish and 90% of the commercial species in south Florida are dependent upon the mangrove system during at least part of their life cycles. Algae. Algae play a vital role in mangrove community food webs.

Sine Saloum Mangrove food web
Food web complexity and robustness decreased from climax>degrading>colonizing> bare, but food web metrics of degrading mangrove forests were similar to the climax and colonizing stages (similar to the findings of Morillo-Velarde et al., 2018). An increase in the diversity of micro-habitats (i.e., habitat heterogeneity) did not affect food web.

A Mangrove Forest Food Chain
As a detritus-based ecosystem, leaf litter from these trees provides the basis for adjacent aquatic and terrestrial food webs. Because most energy and nutrients are biotically stored rather than free in the water or substrate, species diversity of these swamps is directly dependent on primary productivity by mangrove plants.

Mangrove food web of associated fauna Download Scientific Diagram
Foundation of Coastal Food Web. Mangrove forests are important feeding grounds for thousands of species and support a diverse food web. Some organisms will eat the leaves directly, especially crabs and insects, while other decomposers wait for the mangrove leaves to fall to the ground and consume the decaying material. Microbes and fungi among.

Mangrove swamp food chain labquiz
Mangroves Food Web High School 6 NATIONAL COMMON CORE STANDARDS MANGROVES FOOD WEB The following National Common Core Standards can be met teaching EXPLORING THE MANGROVES FOOD WEB: CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.L.8.3 Use knowledge of language and its conventions when writing, speaking, reading, or listening. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.L.8.4 Determine or clarify the meaning of unknown and multiple-meaning words or

A Philippines food chain in a mangrove swamp mangroves ? [place for 4C
The mangrove food web exhibited four trophic levels, a wide consumer δ13C range (~ 10‰), consumer dependence on different carbon sources (mangroves-detritus, microphytobenthos, macroalgae, planktonic sources), and a wide consumer isotopic niche with little overlap. According to MixSiar analyses, microphytobenthos was an important resource.
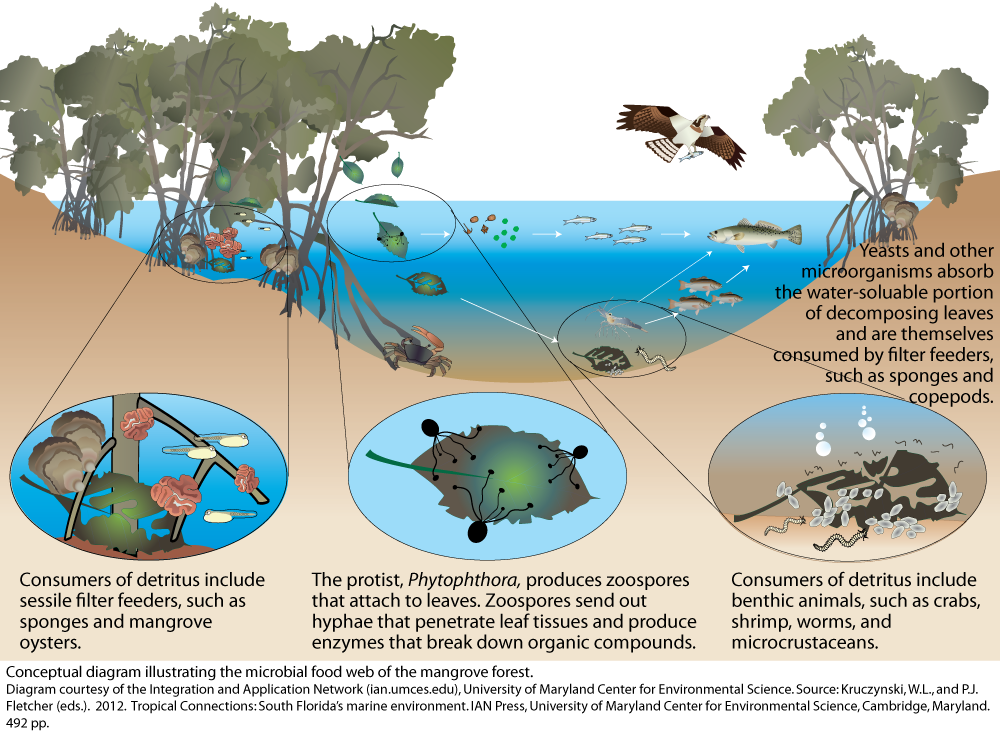
Microbial food web of the mangrove forest University of Maryland
Mangroves form valuable coastal forests but have suffered high deforestation and degradation rates in the past decades (Hamilton and Casey 2016).Restoration of mangroves is a global priority for safeguarding food production, coastal protection, and adaptation to a changing climate (Duarte and other 2013).Worldwide, numerous mangrove restoration programs are underway, for example, in Mexico.
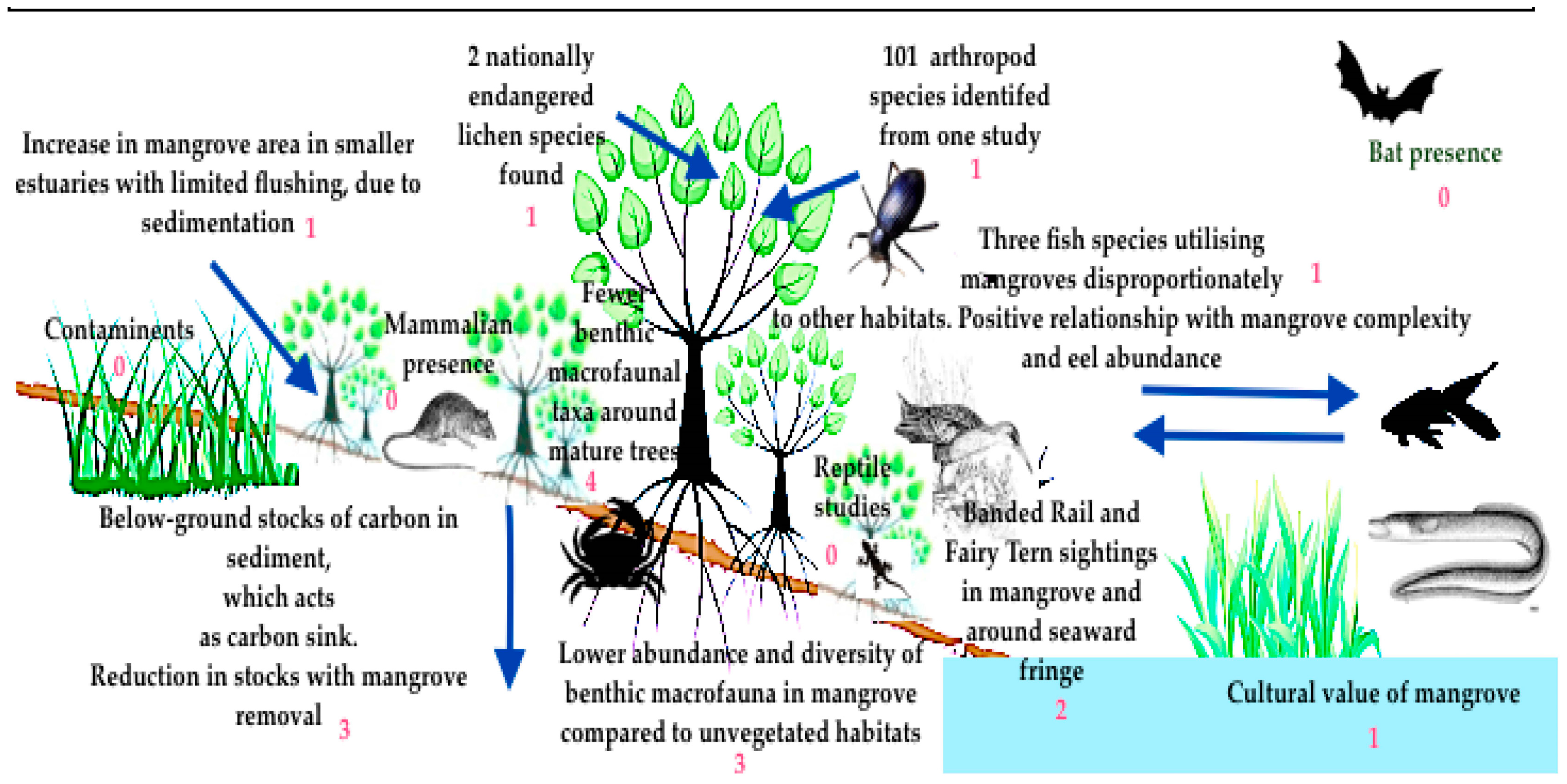
Resources Free FullText A Review on Biodiversity, Ecosystem
Mangrove litter has low value as a food source, and despite the original claims that it fuels coastal productivity, it is mostly recalcitrant (e.g., Baker et al., 2021). The fate of mangrove litter and POC in the coastal zone is a challenge that needs to be quantified, but it appears to be strongly driven by tidal currents (Hyndes et al., 2014).

(PDF) Whole food webs studies Mangroves
Figure 9. A simple food web in a mangrove environment. Zero waste. Nothing is wasted in a mangrove forest. Mangrove plants shed large quantities of nutrient-rich leaves which are either broken down by fungi and bacteria, eaten by crabs that live on the forest floor or are carried into marine and estuarine habitats where they are eaten by a.
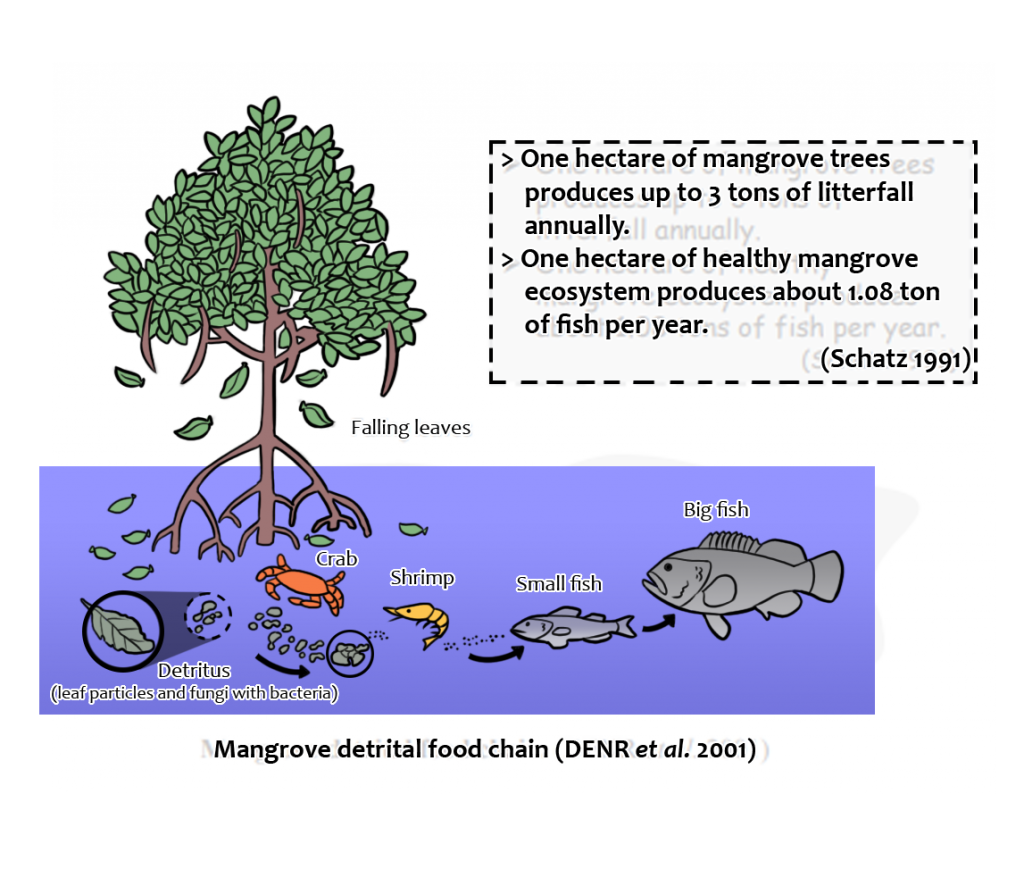
Why are Mangroves important? CCEF
The animals spawn, nest, find shelter, or hunt around mangroves. Together, these animals form a large and complex food web. That's an interconnected system where organisms eat other organisms to get energy (see Mangrove Food Web). People also need mangroves. Large mangrove forests collect sediment, like sand and silt. Sediment builds up.

Food Chains and Webs The Mangrove Ecosystem
coastal food webs, mangrove trophic dynamics must be studied in detail (Bouillon et al., 2002). Under-standing the mangrove food web will allow for more comprehensive management policies that incorporate food web dynamics as well as habitat structure (Gatune et al., 2012; Colleter et al., 2015). Stable isotopes have been extensively used for

aisbiology [licensed for use only] / Ecology
Observed differences between native and invasive mangrove food webs may be due to Hawaiian detritivores being poorly adapted to utilizing the tannin-rich, nitrogen-poor mangrove detritus. In addition, differential utilization of mangrove detritus between native and introduced mangroves may be a consequence of forest age.
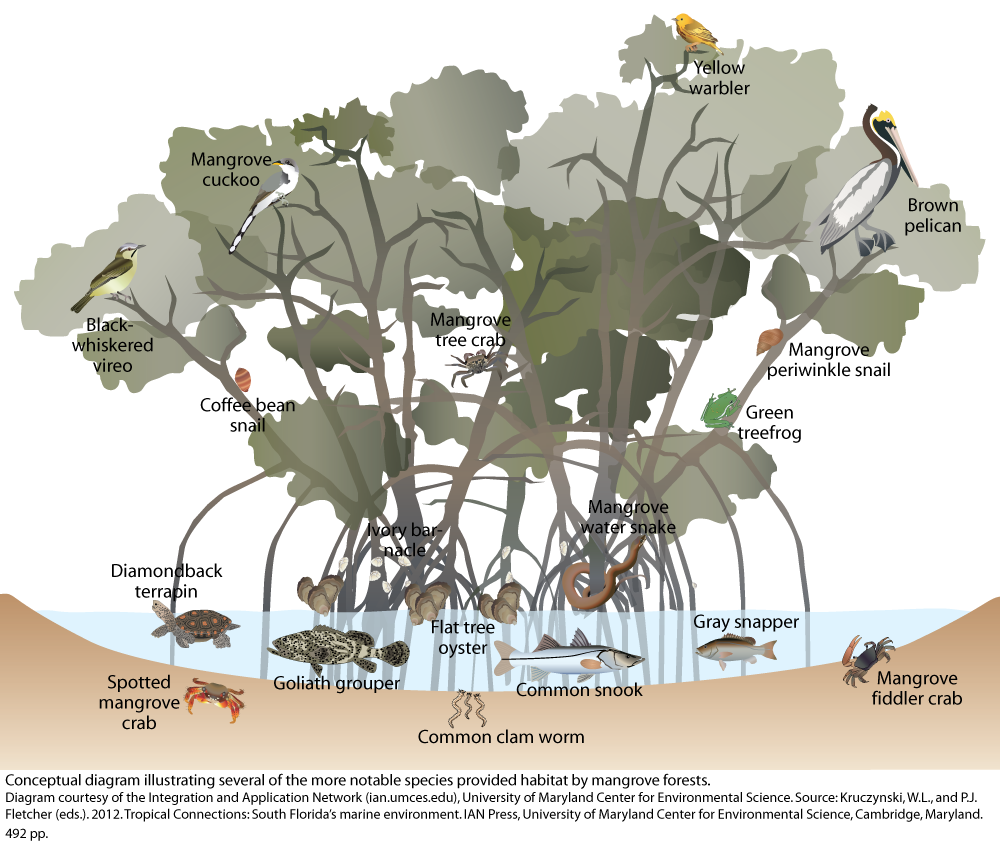
Mangrove forest wildlife Media Library Integration and Application
Stories. An Interconnected Ecosystem: Dive into the Mangrove Food Web. by Nick HammondonApr 14, 2022. Mangroves provide a plethora of ecosystem services that maintain coastal habitat health. One of the most important factors being their ability to maintain the food chain. Take a deep dive with us as we explore the various levels of.
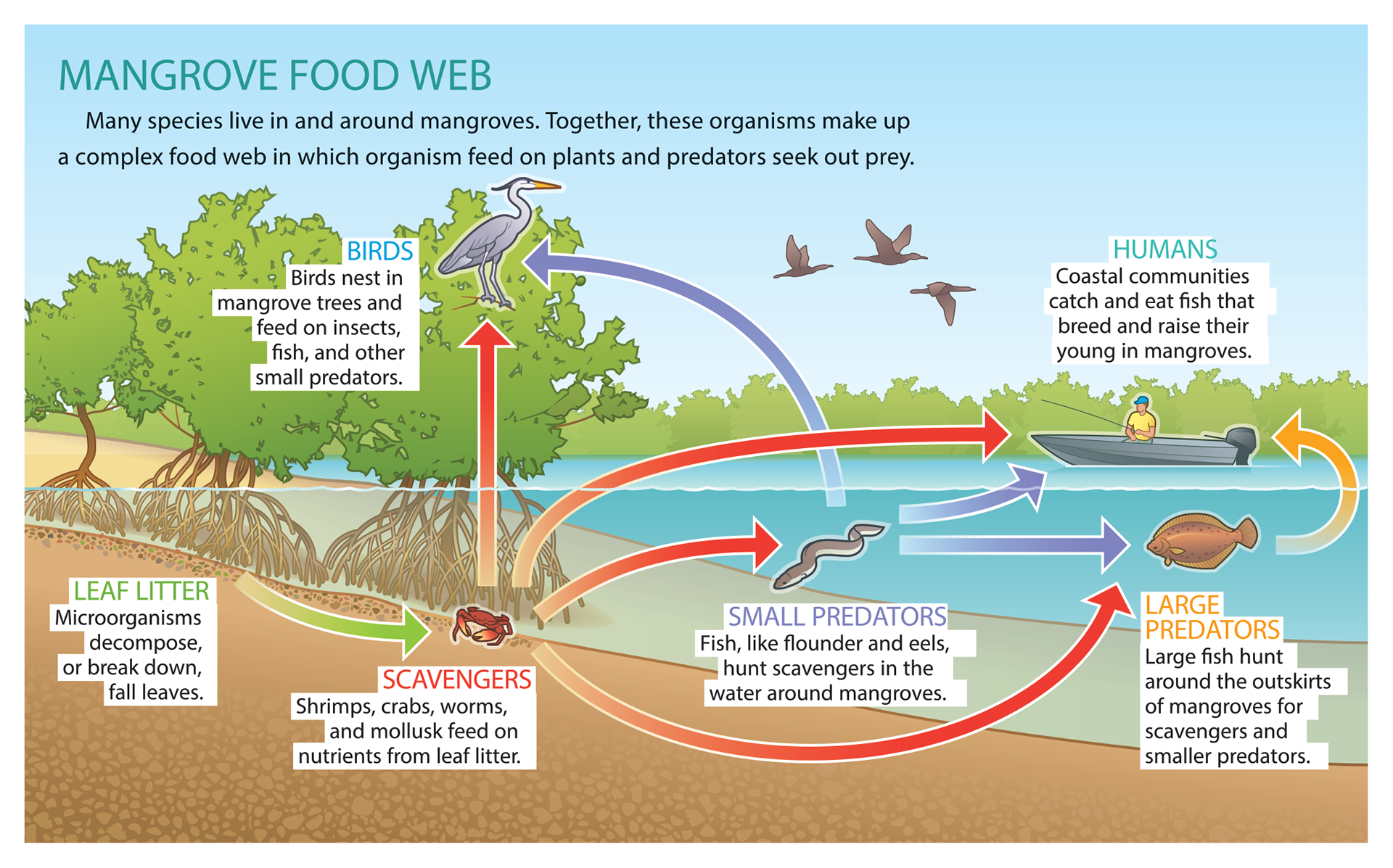
Mangrove Food Web on Behance
Author's personal copy. -. - - - -. PDF | On Jan 1, 2012, Ursula M. Scharler published Whole food webs studies - Mangroves | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate.
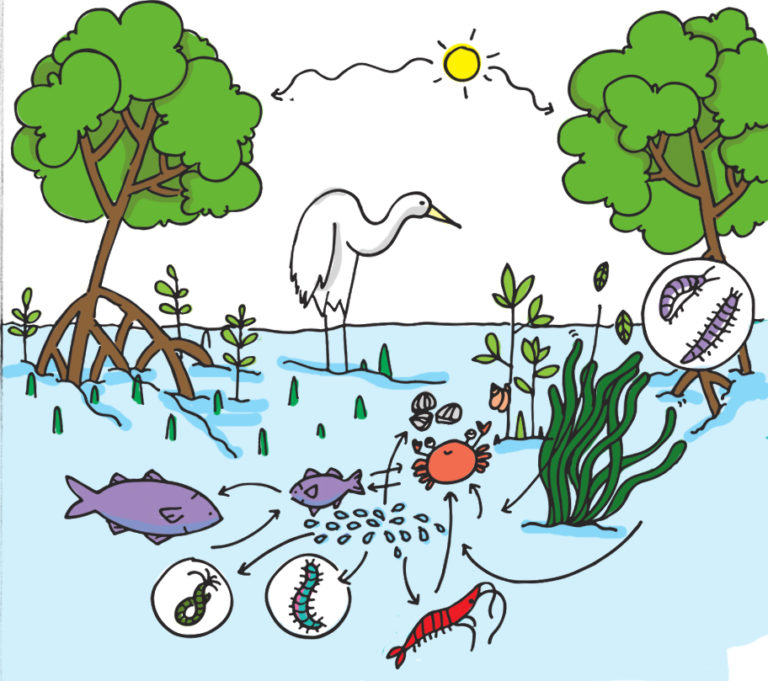
Mangrove_food_web EcoEvoTCD
The bioaccumulation and transfer of Zn in mangrove food webs depend on various factors, including the composition and the complexity of the food web (Croteau et al., 2005; Nfon et al., 2009), while organism traits are also influencing factors, such as their size, age, and sex (Soto-Jiménez, 2011; Griboff et al., 2018).