Gluten Free Info, Gluten Free Health, Gluten Free Food List, What Is

Pasta Sin Gluten, Gluten Free Pasta, Gluten Free Cooking, Gluten Free
Gluten is a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, while glutamate is an amino acid that is naturally present in our bodies and in many foods. While both gluten and glutamate contain the amino acid glutamine, they are not the same thing. Gluten is known to cause problems for people with celiac disease and gluten sensitivity, while glutamate.

Illustration of the glutamateglutamine cycle. (1) When receiving a
Be aware of relying too much on these foods if you are concerned about glutamate consumption: 1. Cheese. You will find the highest levels of glutamate in parmesan and Roquefort cheeses. Parmesan.

The Gluten And Dairy Free Mama's Kitchen
Glutamine is one of the amino acids that make up the gluten protein but both are not the same. One big difference is that we make glutamine. As such, it's classified as a non-essential amino acid. Conversely, the human body does not make gluten. Because of this difference, glutamine supplements are unlikely to produce the same symptoms as.
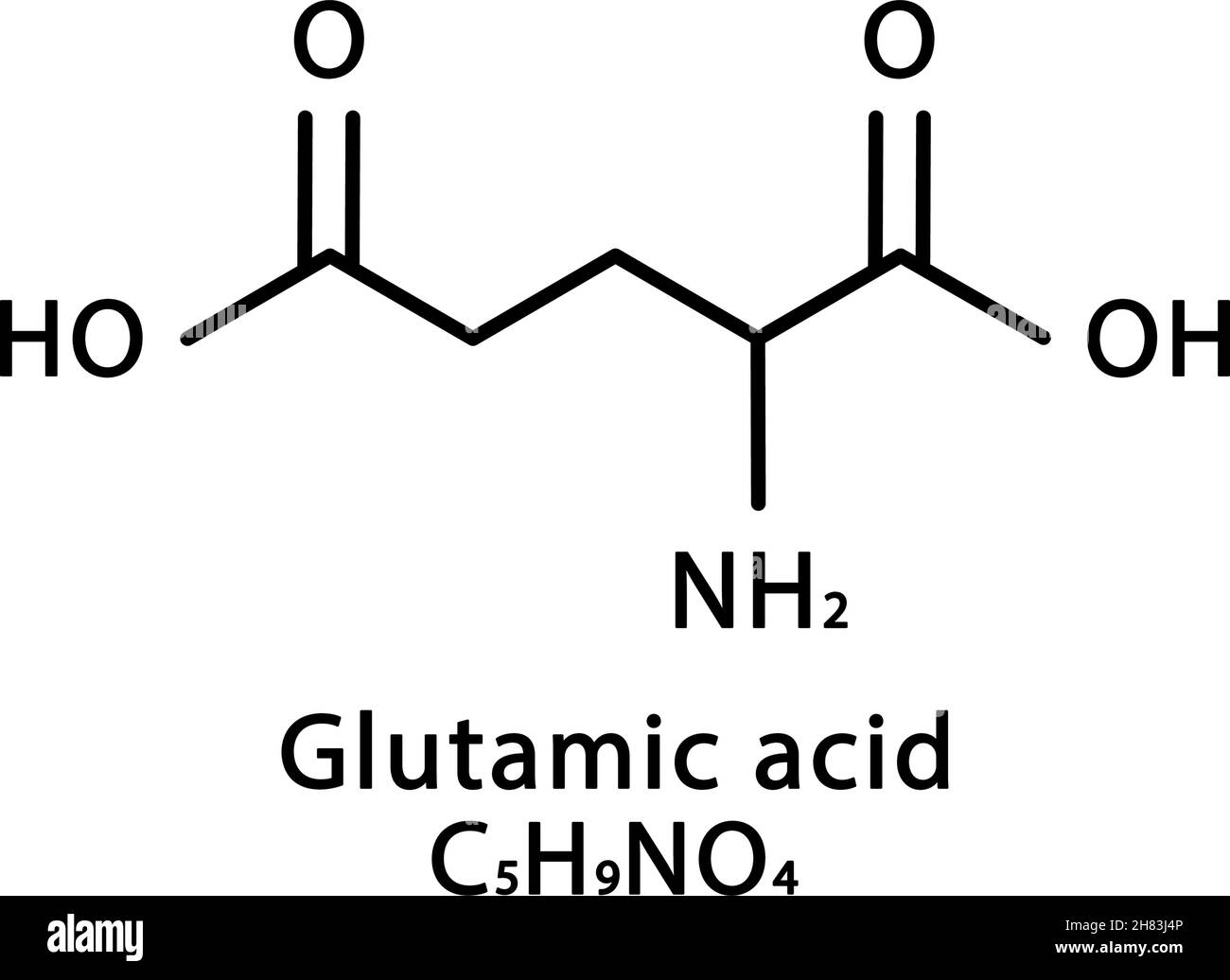
Glutamic acid molecular structure. Glutamate skeletal chemical formula
Autolyzed Yeast, Brewer's Yeast, and Yeast Extract may contain trace amounts of gluten, so they are best avoided. Even though most of these forms of MSG are gluten-free and safe for people with celiac disease, some people have reactions to them, and want to avoid them. celiac disease. gluten-free. gluten-free diet. monosodium glutamate. msg. safe.

The Gluten Alternative
Answer. Yes, monosodium glutamate (MSG) is considered safe on the gluten-free diet. MSG is a sodium salt of glutamic acid that is used as a flavor enhancer in foods. Various starches and sugars may be used as a starting material for MSG, but even if derived from wheat starch it is unlikely that MSG would contain traces of gluten.

Celiac Facts for Patients Lesson 2 Wheat or Gluten Related Symptoms
To increase glutamate production, it may help to add precursors of glutamate (the things your body uses to make it) to your diet or supplement regimen. Some precursors include: 5-HTP: Your body converts 5-HTP into serotonin, and serotonin can enhance GABA activity. 5-HTP is a synthetic form of tryptophan, which is found in turkey.

What Does A Gluten Free Diet Mean keitoohmannkarlic.pages.dev
Misinformation about MSG claiming it's a source of gluten most likely stems back to when glutamate was discovered a century ago. When scientists were first exploring the "umami" flavor that glutamate, one of the most common amino acids found in our bodies, could have, they "extracted" glutamate from protein sources such as kelp and.

Is Gluten Bad for You? Unpacking the Great GlutenFree Debate To Taste
MSG is composed of simply sodium and glutamate. MSG contains only one-third the amount of sodium as table salt. Glutamate and MSG are gluten-free. MSG is safe to consume, according to scientific research and several large regulatory authorities. MSG is not an allergen, according to the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology.

gluten sensitivity vs gluten intolerance What Is Gluten Free, Gluten
Glutamate Metabolism and Functions in the Organism. For the average person, glutamate is associated with the umami taste and it is used in savoury food such as seasonings, condiments, meat products, soups, broths, etc., to enhance their flavour and palatability [].More importantly, glutamate is a non-essential amino acid (AA) highly involved in nitrogen and energy metabolism.
All You Need to Know About Glutamate Chemical Route
Glutamate Vs Gluten. Since glutamate and gluten sound so very similar, they are often confused with one another. However, glutamate and gluten are actually two different things. One has no relation to the other. So when you wonder if glutamate is gluten-free — the answer is yes, but glutamate has nothing to do with gluten. Gluten is a protein.

Gluten Free Info, Gluten Free Health, Gluten Free Food List, What Is
No—glutamate or glutamic acid have nothing to do with gluten. A person with Celiac disease may react to the wheat that may be present in soy sauce, but not to the MSG in the product.

Celiac Disease Archives Life Chiropractic PSL
Noun (obsolete) Fibrin (formerly considered as one of the "animal humours"). *, Bk.I, New York, 2001, p.147: The radical or innate is daily supplied by nourishment, which some call cambium, and make those secondary humours of ros and gluten to maintain it […].; The major protein in cereal grains, especially wheat; responsible for the elasticity in dough and the structure in baked bread.

Glutamate Receptors Cause Calciummediated Toxicity in HD. Glutamate
Glutamate is the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter released by nerve cells in your brain. It plays a major role in learning and memory. For your brain to function properly, glutamate needs to be present in the right concentration in the right places at the right time. Too much glutamate is associated with such diseases as Parkinson's.
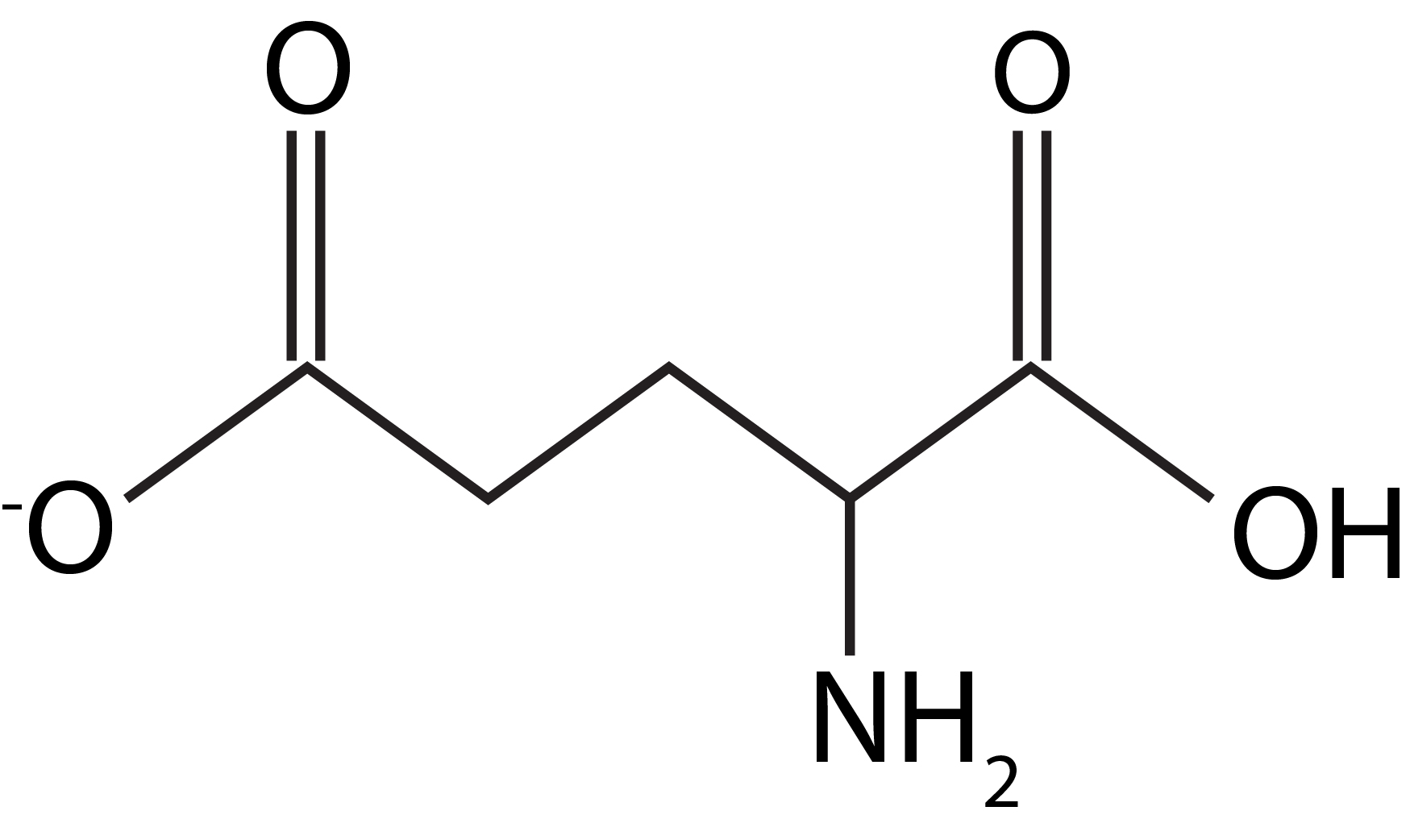
Glutamate Exploring Medicine
German chemist Karl Ritthausen first isolated Glutamic acid from the wheat gluten in 1866, but its chemical structure was identified only in 1890. Chemical Structure of Glutamic acid Identifiers and properties of Glutamic acid. Glutamate and glutamic acid are closely related and often used interchangeably, but there is a chemical distinction.

What is Gluten Free Diet or Recipes for Weight Loss What Gluten Free
Monosodium glutamate is gluten-free. It's made by fermenting sugars or starch and is related to glutamic acid, a naturally-occurring amino acid. However, monosodium glutamate is a highly controversial ingredient. The best healthier alternatives to monosodium glutamate that are also gluten-free include Good & Gather Umami Seasoning Blend.

What is Autolyse? How does it automate bread making? The Flavor Bells
It took a long time to realize that glutamate is a neurotransmitter in part because of its abundance in brain tissue and in part because it is at the crossroad of multiple metabolic pathways (e.g. Erecinska and Silver 1990; Broman et al. 2000; McKenna 2007; Hertz 2013 ). There is 5-15 mmol glutamate per kg brain tissue, depending on the.